1. Cost of Rent: Major cities like São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro tend to have higher rents, while smaller cities and rural areas offer more affordable housing options. On average, rent for a one-bedroom apartment in a city center can range from $300 to $800 per month.
2. Healthcare: Public healthcare is available to immigrants but may have limitations, so many expats opt for private health insurance for more comprehensive and timely care.
3. Transport: Public transportation is common in cities, with options like buses, metro systems, and trams. The cost of transport varies by city but is generally affordable.
4. Food: Brazil offers a rich culinary experience. Eating out at local restaurants and markets is generally affordable. Traditional Brazilian foods like feijoada, acarajé, and acai bowls are popular choices.
5. Culture: Brazil is known for its vibrant culture, including music, dance, and festivals. It's a country that embraces diversity and welcomes people from all over the world.
The average cost of living in Brazil for a single person is approximately $600 to $1,000 per month. This includes expenses like rent, food, transportation, and healthcare.
Pros of Living in Brazil:
• Diverse Culture: Brazil is known for its rich and diverse culture, which includes music, dance, and a variety of regional traditions.
• Natural Beauty: The country boasts stunning natural landscapes, from the Amazon Rainforest to beautiful beaches like Copacabana and Ipanema.
• Culinary Delights: Brazilian cuisine offers a wide range of delicious dishes, and the country is famous for its barbecue, feijoada, and tropical fruits.
• Economic Opportunities: Brazil has a growing economy with opportunities in various sectors, including technology, agriculture, and natural resources.
• Cultural Events: Festivals like Carnival and local celebrations offer vibrant cultural experiences and festivities.
Cons of Living in Brazil:
• Security Concerns: High crime rates, particularly in urban areas, can be a concern, so it's important to take precautions.
• Economic Inequality: Brazil faces significant income inequality, which can impact access to quality education, healthcare, and public services.
• Bureaucracy: Dealing with bureaucracy and administrative processes can be time-consuming and frustrating.
• Traffic and Transportation: Traffic congestion is common in major cities, and public transportation may be inadequate in some areas.
• Cost of Living: The cost of living can vary, but major cities like São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro can be expensive, particularly for housing and education.
1. São Paulo: As Brazil's largest city, São Paulo is a bustling economic and cultural hub. It offers a vibrant nightlife, diverse culinary scene, and numerous job opportunities.
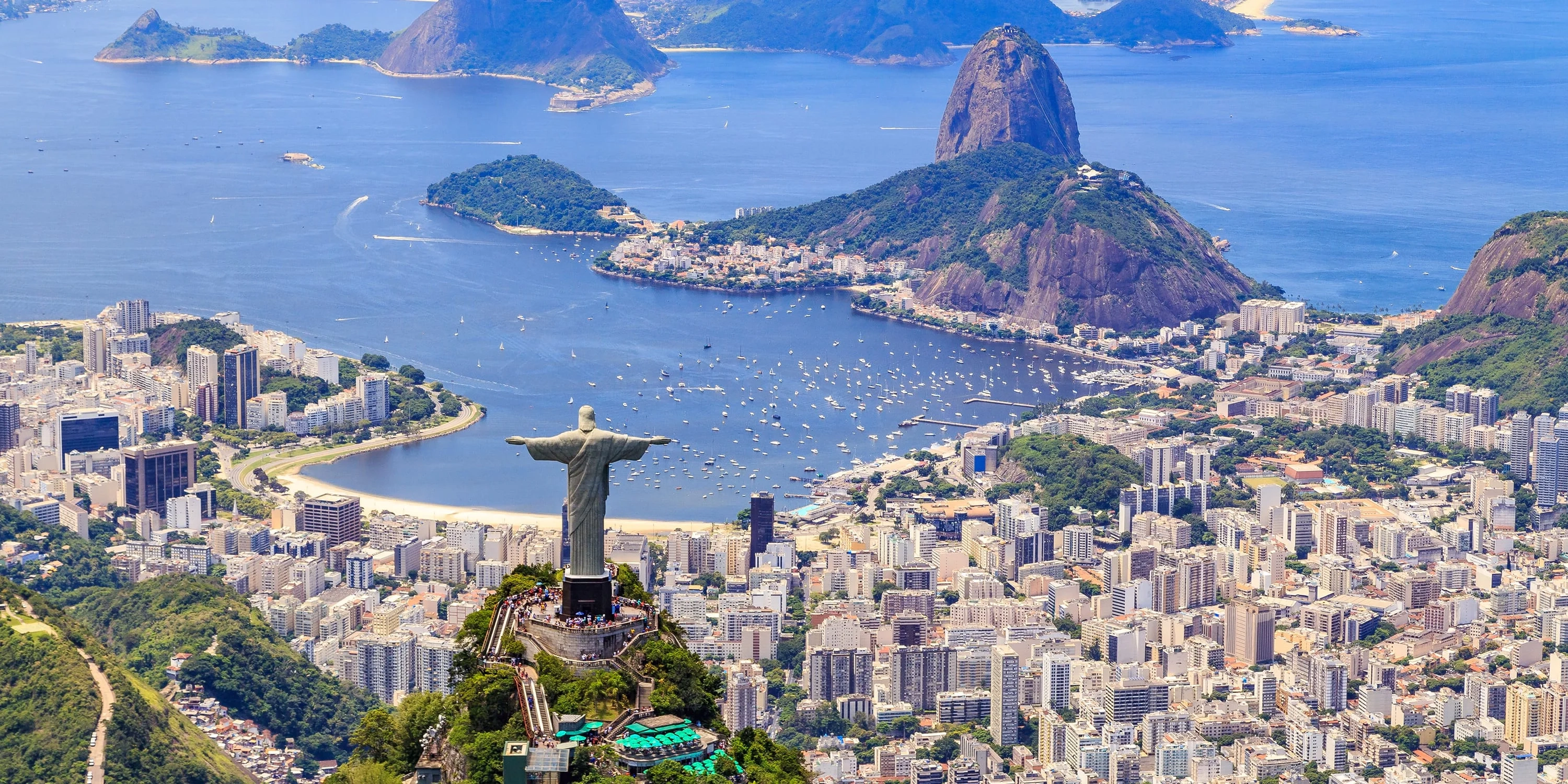
2. Rio de Janeiro: Known for its stunning natural beauty, Rio de Janeiro is famous for its beaches, music, and the iconic Christ the Redeemer statue.
3. Brasília: The capital city of Brazil, Brasília is known for its modernist architecture and is a center for government and bureaucracy. It offers a unique urban design.
4. Belo Horizonte: Belo Horizonte is a major city in southeastern Brazil, known for its pleasant climate, green spaces, and cultural attractions.
5. Florianópolis: Located on an island, Florianópolis offers beautiful beaches, a relaxed lifestyle, and a growing tech industry.
- Research Visa Requirements: Understand the specific visa requirements for your nationality and the purpose of your stay in Brazil. Brazil offers various visa options, including work visas, student visas, and tourist visas. Ensure that you have the correct visa for your situation.
- Learn Portuguese: Portuguese is the official language of Brazil, and while some Brazilians speak English, especially in urban areas, knowledge of Portuguese will be highly beneficial for daily communication and integration.
- Job and Housing Search: If you're moving to Brazil for work, secure a job or employment contract before your arrival. Additionally, find suitable housing in advance to avoid last-minute hassles.
- Healthcare and Insurance: Research healthcare options and consider obtaining private health insurance to ensure access to quality medical care. The public healthcare system, while available to residents, may have limitations.
- Legal and Administrative Tasks: Prepare for bureaucratic processes related to immigration, such as registering with the Federal Police, obtaining an identity card (CPF), and fulfilling tax obligations.